Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Many people know that with heart or cerebral vascular disease, you can have a heart attack or stroke, but they are not aware that PAD, too, can have a dramatic effect on quality of life. To get an idea of how disabling PAD can be, imagine if the arteries in your legs were having angina or if your foot were having a stroke.

Symptoms
The majority of people do not go from having no symptoms to severe vascular pain overnight. However, without an index of suspicion for PAD, most confuse the leg pain — and cramping caused by PAD — with something else. One common example is neurogenic claudication. In this case, leg pain is due to narrowing of the back’s spinal canal (called stenosis).
With neurogenic stenosis, however, pain is not relieved with rest (as expected with PAD), but rather by sitting down. Other nerve disorders such as spinal nerve root irritation or peripheral nerve damage at the end of the hands or feet can mimic PAD as well. Since exercise can make the leg pain from any of these problems worse, the clinical picture can be confusing.
Compounding the diagnostic problem further, both vascular and neurogenic disease can exist together. Your doctor may have recommended that you get an MRI or other imaging study of the back in order to look for stenosis or disc disease. When nothing is found, patients with PAD or one of the other described nerve disorders will continue to suffer unless the physician looks further.
Vascular Claudication Myths
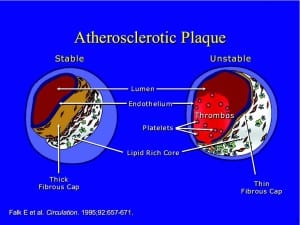
PAD can be present even when other vascular disease is not. The peripheral pulses (pulses in the feet) may be normal, and there may be no visible skin or nail changes present. A family history of vascular disease, an elevated cholesterol, or diet-controlled diabetes may be the only clues.
PAD can occur in the very young (even teenagers) and the very active. Functional claudication can occur with exercise that is perceived by the afflicted as simply getting cramps in the legs or being tired. Blood pressure measurements in the legs can be normal, but pulse volume may be reduced.
Claudication refers to pain in the legs that occurs with exercise, is relieved with rest, and is due to hardening of the arteries in the legs. This is also commonly referred to as Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD). PAD is usually worse in the calf or the foot, although for some people it may be worse in the thigh than in the rest of the leg. At least one-third of people who have PAD also have cardiac or cerebral artery disease.
Non-Surgical Specialty Management
Recent advances in medical management make non-surgical intervention for both the diagnosis and treatment of claudication an excellent treatment choice. Taking blood pressure (vascular Doppler ), pulse volume (vascular Plethysmography), and blood flow (vascular Duplex) readings in various places throughout the arm and leg before and after exercise, valuable information about the presence or absence of PAD can be obtained.
Medicines that improve blood flow and reduce progression of PAD not only offer effective disease management, but also can provide significant pain relief. Exercise, nutrition, and reducing “total load” — factors that do not allow your body to get well, such as smoking — also play an important role.
Even in the presence of neurogenic claudication, treating the PAD component is important. If there is inadequate blood supply, then the nerves will not have enough oxygen and cannot heal or function properly. Naturally, the sooner the diagnosis is made, the more effective medical and preventive treatment will be.
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
PAD Program Sheet (PDF)
Facts About PAD (PDF)
PAD Powerpoint (PPT)