RSD With Distant Effects
RSD with Distant Effects is one of the most recently recognized forms of reflex sympathetic dystrophy. In this case, the afflicted person has sympathetic pain associated with true RSD or any of its subtypes and they have autonomically controlled symptoms related to the internal organs (the vicera). These include, but are not limited to rapid heart rate, change in bowel or bladder function, dizziness, or blurred vision.
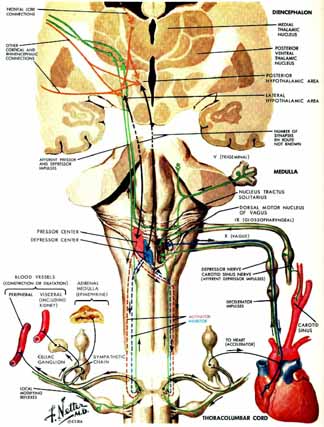
Based upon our own clinical experience — not everyone agrees that the internal organs can become involved — the most common viscera affected include the heart, eyes, and teeth (see the somato-visceral pain chapter). One of the best explanations for the spread of pain from limb to limb is the “table cloth effect.” In this case, the fascia — the sticky stuff in between the skin and meat in chicken — gets pulled, just like a tablecloth, and causes kinks in distant places.
While direct communication of the sympathetic system supplying the internal organs is explanation enough for the spread to internal organs, other possibilities exist. These include body-wide hormone and neuro-transmitter responses to altered autonomic activity and hypothalamic biasing.
In this instance, no “hard” or direct connection between the musculoskeletal system and the viscera exists. Rather a distant form of feedback comes into play. Think of a cell phone tower that has a short or static emitting from within it such that any phone within range of the network is affected.
Treatment for this syndrome is most difficult. It is usually best to focus intervention onto the actual injury site and encourage mobility. More recently success in controlling internal organ system symptoms has been accomplished through use of medications that help stabilize autonomic function for congestive heart failure. Ganglion stabilizing agents (Belladonna) by mouth frequently help, and organ specific intervention, such as artificial tear ducts for dry eyes, has also proven successful.